Funding Support from : SAFE WATER NETWORK INDIA
Project implementing from : 2011 onwards
Grant Amount for 2019-20 : Rs.27,45,527 LOCAL FUNDS & Rs.21,23,382 FOREIGN FUNDS
1. OBJECTIVES:
- “Promotion of Small Water Kiosks in the villages in Telangana” To Establishment of Ijal Stations.
- To bring potable safe drinking water to village communities affected by fluoride and other contaminants in groundwater and safeguarding the health of the poor.
- The initiative seeks to demonstrate the potential for broad scale replication in Telangana.
2. SCALE UP AREA
During the financial year 21 new Safe Water Stations were established across 18 mandals in 9 districts, catering to 5,177 families. Totally there are 167 Safe Water Stations in 145 villages from 95 mandals spread over 15 districts which are catering to 70,496 families.
3. ACTIVITIES CONDUCTED IN 2019-20
| S.NO | Name of the activity | No of Activities | Type of target group | No. of beneficiaries Covered |
| 1 | Re Connectivity | 48 events | User Dropouts | 1,337 |
| 2 | Freedom from diseases | 12 events | School Children | 419 |
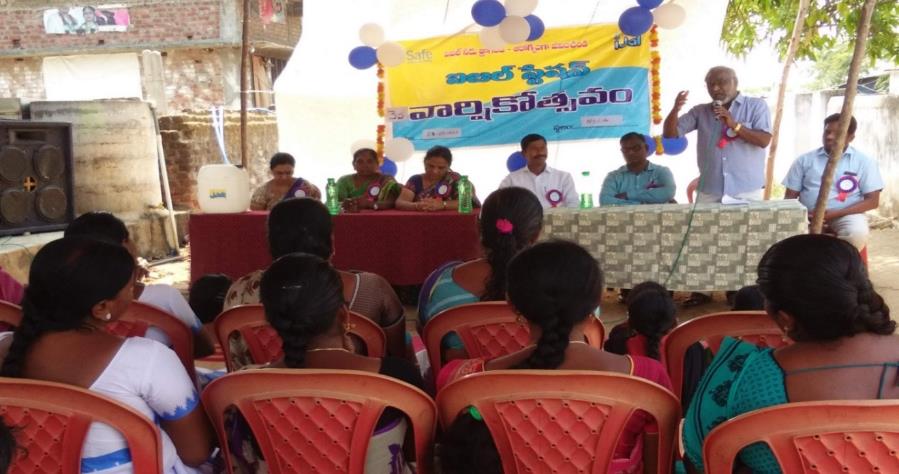
| 3 | Anniversary Celebrations | 09 SWSs | Community Leaders, Officials & Users | 310 |
| 4 | Special Drive for RFID Cards Promotion | 30 events | Households (Users) | 615 |
| 5 | Namaste I Jal | 109 events | Households (Users) | 891 |
| 6 | Awareness on Corona Virus Precautions | 167 events | Users EPs & Operators | 1,250 |
| 7 | Distribution of Masks and Sanitizers | 167 events | EPs & Operators | 334 |
| TOTAL | 542 | 5,156 |
4. Achievements:
- Improve the awareness on Drinking Water in 419 Students
- 24 Hrs Safe water accessibility through ATW System
- Digital Payments
- Plant Down time Reduced to 48 hours
- 390 Members are Employed (145 EPs, 167 Ops, 78 Auto Drivers)
- Facilitating greater involvement of local leaders and village functionaries.
5. Innovations / Best Practices: (2019-20)
- Tools for improving governance:
- Electrolyzed Demo, Charts, Broachers, Pamphlets, Survey formats, Handouts & Templates.
- Canopy
- Can Washer System
- Special care in maintenance in Plant operation
- Reports, guidelines, posters and other knowledge material developed:
- Charts, Broachers, Pamphlets, Survey formats, Handouts & Templates.
- New RMS (Remote Monitoring System) Panel Fitted in all Sites for monitoring
- Monthly Audit system
6. Challenges:
- Shifting & Relocation of Plants from non-beneficial villages has been a big challenge
- Repayments and Digitalization
- Competition with new Pvt. Plant owners.
- Mission Bhageeratha effect, affected water use by the users
- Long Distance of Operational area
7. Learnings:
- Coverage and adoption levels will determine operational self-sufficiency (OSS)
- Intensive efforts are needed to establish community-based units
8. Visitors:
- Local officials and public representatives frequently visited the plants and appreciated the plant functioning and management.
9. Convergence with Line Departments Achieved:
P.R Dept, Municipality, Revenue, Education, Health, ICDS, Police Departments, Local bodies, Public Representatives & Local NGOs.